 5.0 THE CELL, THEORY AND HISTORY OF CELL The cell
5.0 THE CELL, THEORY AND HISTORY OF CELL The cell is defined as the structural and functional unit of living organism, the cell is
the simplest, the smallest and basic unit of life.
All living things are made of cell. Cell is regarded as basic unit of living organism because it carry out all life activities such as "
feeding, reproduction, growth"
CLASSIFICATION OF LIVING ORGANISM i.
Unicellular: These are organism which consist of only one cell. examples "Amoeba, Chlamadomonas, Euglena, Paramecium"
ii.
Multicellular: These are organism which consist of two or more cell. examples "Volvox, Hydra, Spirogyra"
5.1 HISTORY OF CELL ROBERT HOOKE: He is an English scientist who was the father of cell, he was the first human being to discover the
"honey - comb" structure of cell in
1665.
FELIX DUJARDIN: He was french biologist in
1885, discovered that the cell was made up of living substance who named it
"Protoplasm".
MATTHIAS SCHLENDEN: He was a German botanist in
"1838", revealed that the bodies of plant are made up of cell which were describe as unit of life.
THEODOR SCHWANN: He was another German zoologist in
"1839", also discovered that the bodies of all animal are composed of cell
RUDOLF VON VIRCHOW: He was a German biologist in
"1855", concluded his research that all cell come from previously existing cells.
5.2 THE CELL THEORY I. The cell is the structural and functional unit of life.
II. All living organism are made up of cells.
III. All cell come from previously existing cells.
IV. There is not life apart from life of cells.
V. All living organism are either unicellular or multicellular.
5.4 FORMS IN WHICH LIVING CELL EXIST A. AS INDEPENDENT: These are organism which possess only one cell and are capable of living freely on their own. Examples:
"Amoeba, Chlymadomonas, Euglena, Paramecium" 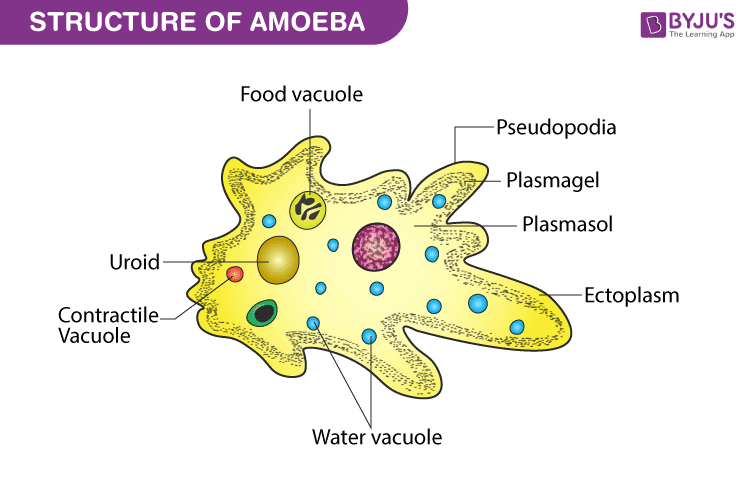 B. AS A COLONY
B. AS A COLONY: These cell form a loosely arranged association of two or more cell, but the cells cannot be differentiate from each other. This aggregation of independent cell is called
"COLONY". Examples: Volvox  C. AS A FILAMENT
C. AS A FILAMENT: Cells are organised into filament in which identical cell are joined end to form unbranched filament. Example:
Spirogyra  5.5 THE PLANT AND ANIMAL CELL
5.5 THE PLANT AND ANIMAL CELL A. { PLANT CELL }
A. { PLANT CELL } * They have chloroplast
* They has definite shape and rectangular
* Has rigid cell wall
* No flexible cell membrane
* Has large vacuole
* Store lipid as oil
* Has nucleus at edge of cytoplasm
B. { ANIMAL CELL } * They have no chloroplast
* Usually spherical or no shape
* Has no cell wall
* Has flexible cell membrane
* Has small vacuole
* Store lipids as fats
* Has nucleus at the center of cytoplasm
5.6 CELL AND ITS ENVIRONMENT DIFFUSION: This is the process by which molecules or ions of a substance move from a region of high concentration to low concentration until they are disturbed.
Factors affecting or controlling diffusion i. State of matter
ii. Molecular size
iii. Difference in concentration
iv. Temperature OSMOSIS: This is the flow of water molecule from the region of low concentration to the region of high concentration through a selectively permeable membrane.
PLASMOLYSIS: This is the outward movement or flow of water from living cell where they are placed in a stronger or hypertonic solution. The process involves the withdrawal of water from living cell.
HAEMOLYSIS: This is the process by which red blood cell become split or burst as a result of too much water passing into it. It occurs when a red blood cell is placed in a weaker or hypertonic solution.
TURGIDITY: This is the condition in which cell absorb plenty of water up to a point where the cell is fully stretched. It occurs when a cell is placed in hypertonic solution.
FLACCIDITY: This is the condition in which plant loss water to their surrounding faster than they can absorb. it occurs when there is no water in the soil.
REVISION EXERCISE
[1] What is diffusion
[2] What is a cell
[3] What is osmosis
[4] What is different between plant and animal cells
[5] What are the history of cells
[6] What is flaccidity and turgidity
[7] Different between Diffusion and osmosis
[8] What is plasmolysis and Haemolysis
[9] List and explain the forms in which cells exist
[10] What are the factors affecting diffusion
[11] Give a well label diagram of Amoeba
[12] Give a well label diagram of Volvox
[13] Give a well label diagram of Euglena
[14] Give a well label diagram of Spirogyra
[15] What are the classification of living organism





